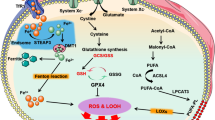
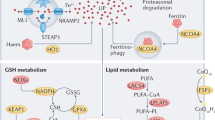
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a leading factor driving mortality worldwide. Iron, an essential trace mineral, is important in numerous biological processes, and its role in CVDs has raised broad discussion for decades. Iron-mediated cell death, namely ferroptosis, has attracted much attention due to its critical role in cardiomyocyte damage and CVDs. Furthermore, ferritinophagy is the upstream mechanism that induces ferroptosis, and is closely related to CVDs. This review aims to delineate the processes and mechanisms of ferroptosis and ferritinophagy, and the regulatory pathways and molecular targets involved in ferritinophagy, and to determine their roles in CVDs. Furthermore, we discuss the possibility of targeting ferritinophagy-induced ferroptosis modulators for treating CVDs. Collectively, this review offers some new insights into the pathology of CVDs and identifies possible therapeutic targets.
摘要
心血管疾病(CVDs)在全球范围内是死亡的主要驱动因素. 铁是一种必需的微量元素, 在多种生物过程中很重要. 几十年来, 铁对心血管疾病的作用引起了广泛的讨论. 由铁介导的细胞死亡方式, 即铁死亡, 在心肌细胞损伤和心血管疾病中发挥着重要的作用, 因此受到广泛关注. 此外, 铁自噬是诱导铁死亡的上游机制, 与心血管疾病密切相关. 本文就铁死亡和铁自噬的过程、 机制、 铁自噬的调控途径和分子靶点进行综述, 并总结其对心血管疾病的作用. 此外, 我们讨论了针对铁自噬诱导的铁死亡调节剂治疗心血管疾病的可能性. 总之, 本综述将为心血管疾病的病理学机制提供新的见解, 并提供一系列潜在治疗靶点.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajoolabady A, Aslkhodapasandhokmabad H, Libby P, et al., 2021. Ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in the management of metabolic diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 32(7):444–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2021.04.010
Aladağ N, Asoğlu R, Ozdemir M, et al., 2021. Oxidants and antioxidants in myocardial infarction (MI): investigation of ischemia modified albumin, malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase and catalase in individuals diagnosed with ST elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-STEMI (NSTEMI). J Med Biochem, 40(3):286–294. https://doi.org/10.5937/jomb0-28879
Allwood MA, Kinobe RT, Ballantyne L, et al., 2014. Heme oxygenase-1 overexpression exacerbates heart failure with aging and pressure overload but is protective against isoproterenol-induced cardiomyopathy in mice. Cardiovasc Pathol, 23(4):231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpath.2014.03.007
Baba Y, Higa JK, Shimada BK, et al., 2018. Protective effects of the mechanistic target of rapamycin against excess iron and ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 314(3):H659–H668. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00452.2017
Bai T, Li MX, Liu YF, et al., 2020. Inhibition of ferroptosis alleviates atherosclerosis through attenuating lipid peroxidation and endothelial dysfunction in mouse aortic endothelial cell. Free Radic Biol Med, 160:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.07.026
Bai YT, Chang R, Wang H, et al., 2018. ENPP2 protects cardiomyocytes from erastin-induced ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 499(1):44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.113
Banjac A, Perisic T, Sato H, et al., 2008. The cystine/cysteine cycle: a redox cycle regulating susceptibility versus resistance to cell death. Oncogene, 27(11):1618–1628. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210796
Bauckman KA, Mysorekar IU, 2016. Ferritinophagy drives uropathogenic Escherichia coli persistence in bladder epithelial cells. Autophagy, 12(5):850–863. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1160176
Beaumont JL, Beaumont V, Lenegre J, 1958. Research on lipid metabolism in human atherosclerosis. II. Multiple aspects of blood lipids in angina pectoris. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol, 3(8):852–868.
Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li ZP, et al., 2019. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature, 575(7784):688–692. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1705-2
Chen XQ, Xu SD, Zhao CX, et al., 2019. Role of TLR4/NADPH oxidase 4 pathway in promoting cell death through autophagy and ferroptosis during heart failure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 516(1):37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.015
Chua ACG, Graham RM, Trinder D, et al., 2007. The regulation of cellular iron metabolism. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci, 44(5–6):413–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408360701428257
Clarke SL, Vasanthakumar A, Anderson SA, et al., 2006. Iron-responsive degradation of iron-regulatory protein 1 does not require the Fe-S cluster. EMBO J, 25(3):544–553. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600954
Corradi M, Mutti A, 2011. Metal ions affecting the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems. Met Ions Life Sci, 8:81–105.
del Rey MQ, Mancias JD, 2019. NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy: a potential link to neurodegeneration. Front Neurosci, 13:238. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00238
Ding M, Feng RT, Wang SY, et al., 2006. Cyanidin-3-glucoside, a natural product derived from blackberry, exhibits chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic activity. J Biol Chem, 281(25):17359–17368. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M600861200
Dodd S, Dean O, Copolov DL, et al., 2008. N-Acetylcysteine for antioxidant therapy: pharmacology and clinical utility. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 8(12):1955–1962. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728220802517901
Doll S, Freitas FP, Shah R, et al., 2019. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature, 575(7784):693–698. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1707-0
Drysdale J, Arosio P, Invernizzi R, et al., 2002. Mitochondrial ferritin: a new player in iron metabolism. Blood Cells Mol Dis, 29(3):376–383. https://doi.org/10.1006/bcmd.2002.0577
Erber LN, Luo A, Gong Y, et al., 2021. Iron deficiency reprograms phosphorylation signaling and reduces O-GlcNAc pathways in neuronal cells. Nutrients, 13(1):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010179
Fang XX, Wang H, Han D, et al., 2019. Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 116(7):2672–2680. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1821022116
Fang XX, Cai ZX, Wang H, et al., 2020. Loss of cardiac ferritin H facilitates cardiomyopathy via Slc7a11-mediated ferroptosis. Circ Res, 127(4):486–501. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316509
Fang XX, Ardehali H, Min JX, et al., 2023. The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol, 20:7–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-022-00735-4
Feng YS, Madungwe NB, Aliagan ADI, et al., 2019. Liproxstatin-1 protects the mouse myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury by decreasing VDAC1 levels and restoring GPX4 levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 520(3):606–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.006
Fisher SA, Brunskill SJ, Doree C, et al., 2013a. Desferrioxamine mesylate for managing transfusional iron overload in people with transfusion-dependent thalassaemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, (8):CD004450. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004450.pub3
Fisher SA, Brunskill SJ, Doree C, et al., 2013b. Oral deferiprone for iron chelation in people with thalassaemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, (8):CD004839. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004839.pub3
Fleming MD, 2008. The regulation of hepcidin and its effects on systemic and cellular iron metabolism. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program, 2008(1):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2008.1.151
Fox NG, Das D, Chakrabarti M, et al., 2015. Frataxin accelerates [2Fe-2S] cluster formation on the human Fe-S assembly complex. Biochemistry, 54(25):3880–3889. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi5014497
Fuhrmann DC, Mondorf A, Beifuß J, et al., 2020. Hypoxia inhibits ferritinophagy, increases mitochondrial ferritin, and protects from ferroptosis. Redox Biol, 36:101670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101670
Fujimaki M, Furuya N, Saiki S, et al., 2019. Iron supply via NCOA4-mediated ferritin degradation maintains mitochondrial functions. Mol Cell Biol, 39(14):e00010–19. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00010-19
Gan BY, 2021. Mitochondrial regulation of ferroptosis. J Cell Biol, 220(9):e202105043. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202105043
Gan BY, 2022. ACSL4, PUFA, and ferroptosis: new arsenal in anti-tumor immunity. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 7:128. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01004-z
Gao GF, Chang YZ, 2014. Mitochondrial ferritin in the regulation of brain iron homeostasis and neurodegenerative diseases. Front Pharmacol, 5:19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2014.00019
Gao JY, Zhou QL, Wu D, et al., 2021. Mitochondrial iron metabolism and its role in diseases. Clin Chim Acta, 513:6–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.12.005
Gao Z, Gao Q, Lv XD, 2020. MicroRNA-668-3p protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation in a rat H9c2 cardiomyocyte model of ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting the stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit, 26:e919601. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.919601
Gianazza E, Brioschi M, Fernandez AM, et al., 2021. Lipid peroxidation in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal, 34(1):49–98. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2019.7955
Graham L, Orenstein JM, 2007. Processing tissue and cells for transmission electron microscopy in diagnostic pathology and research. Nat Protoc, 2(10):2439–2450. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.304
Gryzik M, Asperti M, Denardo A, et al., 2021. NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy promotes ferroptosis induced by erastin, but not by RSL3 in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 1868(2):118913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118913
Gu CZ, Chang WJ, Wu JL, et al., 2022. NCOA4: an immunomodulation-related prognostic biomarker in colon adenocarcinoma and pan-cancer. J Oncol, 2022:5242437. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5242437
Guo JD, Zhao X, Li Y, et al., 2018. Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease (Review). Int J Mol Med, 41(4):1817–1825. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3406
Guo ZM, Ran QT, Roberts LJ II, et al., 2008. Suppression of atherogenesis by overexpression of glutathione peroxidase-4 in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Free Radic Biol Med, 44(3):343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.09.009
Han C, Liu YY, Dai RJ, et al., 2020. Ferroptosis and its potential role in human diseases. Front Pharmacol, 11:239. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00239
Han JW, Kang C, Kim Y, et al., 2020. Isoproterenol-induced hypertrophy of neonatal cardiac myocytes and H9c2 cell is dependent on TRPC3-regulated Cav1.2 expression. Cell Calcium, 92:102305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102305
Han XJ, Zhang J, Liu J, et al., 2023. Targeting ferroptosis: a novel insight against myocardial infarction and ischemia-reperfusion injuries. Apoptosis, 28:108–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01785-2
Henninger C, Fritz G, 2018. Statins in anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: Rac and Rho, and the heartbreakers. Cell Death Dis, 8:e2564. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.418
Hinman A, Holst CR, Latham JC, et al., 2018. Vitamin E hydroquinone is an endogenous regulator of ferroptosis via redox control of 15-lipoxygenase. PLoS ONE, 13(8):e0201369. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201369
Hollenberg SM, Singer M, 2021. Pathophysiology of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol, 18(6):424–434. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-020-00492-2
Hou W, Xie YC, Song XX, et al., 2016. Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy, 12(8):1425–1428. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1187366
Huang TF, Sun YJ, Li YL, et al., 2018. Growth inhibition of a novel iron chelator, DpdtC, against hepatoma carcinoma cell lines partly attributed to ferritinophagy-mediated lysosomal ROS generation. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018:4928703. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4928703
Imai H, Matsuoka M, Kumagai T, et al., 2017. Lipid peroxidation-dependent cell death regulated by GPx4 and ferroptosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, 403:143–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/82_2016_508
Ito J, Omiya S, Rusu MC, et al., 2021. Iron derived from autophagy-mediated ferritin degradation induces cardiomyocyte death and heart failure in mice. eLife, 10:e62174. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.62174
Javadov S, 2022. Mitochondria and ferroptosis. Curr Opin Physiol, 25:100483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cophys.2022.100483
Jiang JJ, Zhang GF, Zheng JY, et al., 2022. Targeting mitochondrial ROS-mediated ferroptosis by quercetin alleviates high-fat diet-induced hepatic lipotoxicity. Front Pharmacol, 13:876550. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.876550
Jiang XJ, Stockwell BR, Conrad M, 2021. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 22(4):266–282. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
Jin T, He Q, Cheng C, et al., 2022. UAMC-3203 or/and deferoxamine improve post-resuscitation myocardial dysfunction through suppressing ferroptosis in a rat model of cardiac arrest. Shock, 57(3):344–350. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000001869
Kane MD, Schwarz RD, St. Pierre L, et al., 1999. Inhibitors of V-type ATPases, bafilomycin A1 and concanamycin A, protect against β-amyloid-mediated effects on 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction. J Neurochem, 72(5):1939–1947. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0721939.x
Kang H, Han MR, Xue J, et al., 2019. Renal clearable nanochelators for iron overload therapy. Nat Commun, 10:5134. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13143-z
Kitakata H, Endo J, Ikura H, et al., 2022. Therapeutic targets for DOX-induced cardiomyopathy: role of apoptosis vs. ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci, 23(3):1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031414
Koleini N, Shapiro JS, Geier J, et al., 2021. Ironing out mechanisms of iron homeostasis and disorders of iron deficiency. J Clin Invest, 131(11):e148671. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI148671
Kollara A, Brown TJ, 2012. Expression and function of nuclear receptor co-activator 4: evidence of a potential role independent of co-activator activity. Cell Mol Life Sci, 69(23):3895–3909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1000-y
Kopinski PK, Singh LN, Zhang SP, et al., 2021. Mitochondrial DNA variation and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 21(7):431–445. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-021-00358-w
Lai YF, Dong J, Wu Y, et al., 2022. Lipid peroxides mediated ferroptosis in electromagnetic pulse-induced hippocampal neuronal damage via inhibition of GSH/GPX4 axis. Int J Mol Sci, 23(16):9277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169277
Lakhal-Littleton S, 2019. Iron deficiency as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Pharmaceuticals, 12(3):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12030125
Lan HY, Gao Y, Zhao ZY, et al., 2022. Ferroptosis: redox imbalance and hematological tumorigenesis. Front Oncol, 12:834681. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.834681
Lee HL, Hee SW, Hsuan CF, et al., 2021. A novel ALDH2 activator AD-9308 improves diastolic and systolic myocardial functions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Antioxidants, 10(3):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030450
Lee JC, Chiang KC, Feng TH, et al., 2016. The iron chelator, Dp44mT, effectively inhibits human oral squamous cell carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Sci, 17(9):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091435
Lee JY, Kim WK, Bae KH, et al., 2021. Lipid metabolism and ferroptosis. Biology, 10(3):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030184
Lee YS, Lee DH, Choudry HA, et al., 2018. Ferroptosis-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress: cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res, 16(7):1073–1076. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0055
Lei G, Zhuang L, Gan BY, 2022. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 22(7):381–396. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-022-00459-0
Leng YL, Luo X, Yu JY, et al., 2022. Ferroptosis: a potential target in cardiovascular disease. Front Cell Dev Biol, 9:813668. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.813668
Li C, Sun GC, Chen BL, et al., 2021. Nuclear receptor coactivator 4-mediated ferritinophagy contributes to cerebral ischemia-induced ferroptosis in ischemic stroke. Pharmacol Res, 174:105933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105933
Li C, Wu ZY, Xue H, et al., 2022. Ferroptosis contributes to hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats: role of the SIRT1/Nrf2/GPx4 signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther, 28(12):2268–2280. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13973
Li FJ, Long HZ, Zhou ZW, et al., 2022. System Xc−/GSH/GPX4 axis: an important antioxidant system for the ferroptosis in drug-resistant solid tumor therapy. Front Pharmacol, 13:910292. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.910292
Li N, Wang W, Zhou H, et al., 2020. Ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis is involved in sepsis-induced cardiac injury. Free Radic Biol Med, 160:303–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.08.009
Li N, Jiang WY, Wang W, et al., 2021. Ferroptosis and its emerging roles in cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol Res, 166:105466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105466
Li Q, Han XN, Lan X, et al., 2017. Inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis protects hemorrhagic brain. JCI Insight, 2(7):e90777. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.90777
Li SY, Wang R, Wang YX, et al., 2022. Ferroptosis: a new insight for treatment of acute kidney injury. Front Pharmacol, 13:1065867. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1065867
Li SZ, Zhang XY, 2021. Iron in cardiovascular disease: challenges and potentials. Front Cardiovasc Med, 8:707138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.707138
Li XQ, Lozovatsky L, Sukumaran A, et al., 2020. NCOA4 is regulated by HIF and mediates mobilization of murine hepatic iron stores after blood loss. Blood, 136(23):2691–2702. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2020006321
Lin MM, Liu N, Qin ZH, et al., 2022. Mitochondrial-derived damage-associated molecular patterns amplify neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 43(10):2439–2447. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00879-6
Lin PL, Tang HH, Wu SY, et al., 2020. Saponin formosanin C-induced ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Antioxidants, 9(8):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080682
Littarru GP, Langsjoen P, 2007. Coenzyme Q10 and statins: biochemical and clinical implications. Mitochondrion, 7:S168–S174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2007.03.002
Liu B, Zhao CX, Li HK, et al., 2018. Puerarin protects against heart failure induced by pressure overload through mitigation of ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 497(1):233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.061
Liu JP, Cen SY, Xue ZA, et al., 2022. A class of disulfide compounds suppresses ferroptosis by stabilizing GPX4. ACS Chem Biol, 17(12):3389–3406. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.2c00445
Liu M, Kong XY, Yao Y, et al., 2022. The critical role and molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis in antioxidant systems: a narrative review. Ann Transl Med, 10(6):368. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-6942
Liu MR, Zhu WT, Pei DS, 2021. System Xc−: a key regulatory target of ferroptosis in cancer. Invest New Drugs, 39(4):1123–1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01070-0
Liu MZ, Kong N, Zhang GY, et al., 2022. The critical role of ferritinophagy in human disease. Front Pharmacol, 13:933732. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.933732
Liu PF, Feng YT, Li HW, et al., 2020. Ferrostatin-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 25:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-020-00205-0
Liu R, Zhi XY, Zhong Q, 2015. ATG14 controls SNARE-mediated autophagosome fusion with a lysosome. Autophagy, 11(5):847–849. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1037549
Liu X, Du SW, Wang SD, et al., 2022. Ferroptosis in osteosarcoma: a promising future. Front Oncol, 12:1031779. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.1031779
Liu XM, Li DL, Pi WH, et al., 2022. LCZ696 protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting ferroptosis via AKT/SIRT3/SOD2 signaling pathway activation. Int Immunopharmacol, 113:109379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109379
Liu Y, Wang W, Li YY, et al., 2015. The 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton confers neuroprotection against glutamate oxidative damage by inhibiting ferroptosis. Biol Pharm Bull, 38(8):1234–1239. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b15-00048
Liu YC, Zeng LP, Yang Y, et al., 2020. Acyl-CoA thioesterase 1 prevents cardiomyocytes from Doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis via shaping the lipid composition. Cell Death Dis, 11(9):756. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02948-2
Lu LQ, Wu D, Li LF, et al., 2017. Apelin/APJ system: a bifunctional target for cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Cardiol, 230:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.215
Lu LQ, Tian J, Luo XJ, et al., 2021. Targeting the pathways of regulated necrosis: a potential strategy for alleviation of cardio-cerebrovascular injury. Cell Mol Life Sci, 78:63–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03587-8
Luan Y, Luan Y, Feng Q, et al., 2021a. Emerging role of mitophagy in the heart: therapeutic potentials to modulate mitophagy in cardiac diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021:3259963. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3259963
Luan Y, Ren KD, Luan Y, et al., 2021b. Mitochondrial dynamics: pathogenesis and therapeutic targets of vascular diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med, 8:770574. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.770574
Luan Y, Luan Y, Yuan RX, et al., 2021c. Structure and function of mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAMs) and their role in cardiovascular diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021:4578809. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4578809
Luo Y, Apaijai N, Liao SC, et al., 2022. Therapeutic potentials of cell death inhibitors in rats with cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury. J Cell Mol Med, 26(8):2462–2476. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17275
Lv XH, Jiang HH, Li BG, et al., 2014. The crucial role of Atg5 in cortical neurogenesis during early brain development. Sci Rep, 4:6010. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06010
Lv YH, Wu MY, Wang Z, et al., 2022. Ferroptosis: from regulation of lipid peroxidation to the treatment of diseases. Cell Biol Toxicol, 39:827–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-022-09778-2
Ma TY, Du JT, Zhang YF, et al., 2022. GPX4-independent ferroptosis—a new strategy in disease’s therapy. Cell Death Discov, 8:434. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-022-01212-0
Maine MD, 1979. Role of trace metals in regulation of cellular heme and hemoprotein metabolism: sensitizing effects of chronic iron treatment on acute gold toxicity. Drug Metab Rev, 9(2):237–255. https://doi.org/10.3109/03602537908993893
Mancias JD, Vaites LP, Nissim S, et al., 2015. Ferritinophagy via NCOA4 is required for erythropoiesis and is regulated by iron dependent HERC2-mediated proteolysis. Elife, 4:e10308. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.10308
Mao C, Liu XG, Zhang YL, et al., 2021. DHODH-mediated ferroptosis defence is a targetable vulnerability in cancer. Nature, 593(7860):586–590. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03539-7
Meng ZJ, Liang HP, Zhao JL, et al., 2021. HMOX1 upregulation promotes ferroptosis in diabetic atherosclerosis. Life Sci, 284:119935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119935
Minakaki G, Menges S, Kittel A, et al., 2018. Autophagy inhibition promotes SNCA/alpha-synuclein release and transfer via extracellular vesicles with a hybrid autophagosome-exosome-like phenotype. Autophagy, 14(1):98–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2017.1395992
Mishima E, Ito J, Wu ZJ, et al., 2022. A non-canonical vitamin K cycle is a potent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature, 608(7924):778–783. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05022-3
Mo YS, Duan LN, Yang YN, et al., 2021. Nanoparticles improved resveratrol brain delivery and its therapeutic efficacy against intracerebral hemorrhage. Nanoscale, 13(6):3827–3840. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr06249a
Mohanty SK, Donnelly B, Temple H, et al., 2021. High mobility group box 1 release by cholangiocytes governs biliary atresia pathogenesis and correlates with increases in afflicted infants. Hepatology, 74(2):864–878. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31745
Omiya S, Ito J, Otsu L, 2021. Labile iron derived from autophagy-mediated ferritin degradation in cardiomyocytes under pressure overload increases myocardial oxidative stress and develops heart failure in mice. Eur Heart J, 42(Suppl_1):ehab724.0747. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab724.0747
Park E, Chung SW, 2019. ROS-mediated autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation. Cell Death Dis, 10(11):822. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2064-5
Park TJ, Park JH, Lee GS, et al., 2019. Quantitative proteomic analyses reveal that GPX4 downregulation during myocardial infarction contributes to ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Cell Death Dis, 10:835. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2061-8
Pesce E, Sondo E, Ferrera L, et al., 2018. The autophagy inhibitor spautin-1 antagonizes rescue of mutant CFTR through an autophagy-independent and USP13-mediated mechanism. Front Pharmacol, 9:1464. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01464
Peyssonnaux C, Zinkernagel AS, Schuepbach RA, et al., 2007. Regulation of iron homeostasis by the hypoxiainducible transcription factors (HIFs). J Clin Invest, 117(7):1926–1932. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI31370
Philpott CC, 2020. Iron on the move: mobilizing liver iron via NCOA4. Blood, 136(23):2604–2605. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2020007971
Prasad MK, Mohandas S, Mohanram RK, 2023. Role of ferroptosis inhibitors in the management of diabetes. Bio-Factors, 49(2):270–296. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1920
Pridham KJ, Varghese RT, Sheng Z, 2017. The role of class IA phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunits in glioblastoma. Front Oncol, 7:312. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2017.00312
Protchenko O, Baratz E, Jadhav S, et al., 2021. Iron chaper-one poly rC binding protein 1 protects mouse liver from lipid peroxidation and steatosis. Hepatology, 73(3):1176–1193. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31328
Puig S, Ramos-Alonso L, Romero AM, et al., 2017. The elemental role of iron in DNA synthesis and repair. Metallomics, 9(11):1483–1500. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7mt00116a
Pullarkat V, Meng Z, Donohue C, et al., 2014. Iron chelators induce autophagic cell death in multiple myeloma cells. Leuk Res, 38(8):988–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2014.06.005
Qi RG, Wang YH, Bruno PM, et al., 2017. Nanoparticle conjugates of a highly potent toxin enhance safety and circumvent platinum resistance in ovarian cancer. Nat Commun, 8:2166. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02390-7
Qin X, Tang QH, Jiang XJ, et al., 2020. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce ferroptotic neuronal cell death in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine, 15:5299–5315. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S250367
Qin X, Zhang J, Wang B, et al., 2021. Ferritinophagy is involved in the zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced ferroptosis of vascular endothelial cells. Autophagy, 17(12):4266–4285. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1911016
Qin YH, Qiao Y, Wang D, et al., 2021. Ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and potential applications. Biomed Pharmacother, 141:111872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111872
Reeves AR, Sansbury BE, Pan MX, et al., 2021. Myeloid-specific deficiency of long-chain acyl CoA synthetase 4 reduces inflammation by remodeling phospholipids and reducing production of arachidonic acid-derived proinflammatory lipid mediators. J Immunol, 207(11):2744–2753. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.2100393
Ren YF, Yang MW, Wang XD, et al., 2022. ELAV-like RNA binding protein 1 regulates osteogenesis in diabetic osteoporosis: involvement of divalent metal transporter 1. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 546:111559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2022.111559
Rockfield S, Flores I, Nanjundan M, 2018. Expression and function of nuclear receptor coactivator 4 isoforms in transformed endometriotic and malignant ovarian cells. Oncotarget, 9(4):5344–5367. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.23747
Ryu MS, Duck KA, Philpott CC, 2018. Ferritin iron regulators, PCBP1 and NCOA4, respond to cellular iron status in developing red cells. Blood Cells Mol Dis, 69:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2017.09.009
Santana-Codina N, Mancias JD, 2018. The role of NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy in health and disease. Pharmaceuticals, 11 (4): 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11040114
Santana-Codina N, Gableske S, del Rey MQ, et al., 2019. NCOA4 maintains murine erythropoiesis via cell autonomous and non-autonomous mechanisms. Haematologica, 104(7):1342–1354. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.204123
Santana-Codina N, Gikandi A, Mancias JD, 2021. The role of NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy in ferroptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol, 1301:41–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62026-4_4
Santana-Codina N, del Rey MQ, Kapner KS, et al., 2022. NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy is a pancreatic cancer dependency via maintenance of iron bioavailability for iron-sulfur cluster proteins. Cancer Discov, 12(9):2180–2197. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0043
Sasazawa Y, Kanagaki S, Tashiro E, et al., 2012. Xanthohumol impairs autophagosome maturation through direct inhibition of valosin-containing protein. ACS Chem Biol, 7(5):892–900. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb200492h
Savarese G, von Haehling S, Butler J, et al., 2023. Iron deficiency and cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J, 44(1):14–27. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehac569
Savaryn JP, Reitsma JM, Bigley TM, et al., 2013. Human cytomegalovirus pUL29/28 and pUL38 repression of p53-regulated p21CIP1 and caspase 1 promoters during infection. J Virol, 87(5):2463–2474. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01926-12
Sevrioukova IF, 2011. Apoptosis-inducing factor: structure, function, and redox regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal, 14(12):2545–2579. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3445
Shi Q, Liu R, Chen L, 2022. Ferroptosis inhibitor ferrostatin-1 alleviates homocysteine-induced ovarian granulosa cell injury by regulating TET activity and DNA methylation. Mol Med Rep, 25(4):130. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2022.12645
Shibata Y, Yasui H, Higashikawa K, et al., 2019. Erastin, a ferroptosis-inducing agent, sensitized cancer cells to X-ray irradiation via glutathione starvation in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE, 14(12):e0225931. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0225931
Shindo M, Torimoto Y, Saito H, et al., 2006. Functional role of DMT1 in transferrin-independent iron uptake by human hepatocyte and hepatocellular carcinoma cell, HLF. Hepatol Res, 35(3):152–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hepres.2006.03.011
Shizukuda Y, Matoba S, Mian OY, et al., 2005. Targeted disruption of p53 attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in mice. Mol Cell Biochem, 273(1–2):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-5905-8
Shroff EH, Eberlin LS, Dang VM, et al., 2015. MYC oncogene overexpression drives renal cell carcinoma in a mouse model through glutamine metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 112(21):6539–6544. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1507228112
Silva MM, de Souza-Neto FP, de Jesus ICG, et al., 2021. Alamandine improves cardiac remodeling induced by transverse aortic constriction in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 320(1):H352–H363. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00328.2020
Silvain J, Zeitouni M, Paradies V, et al., 2021. Procedural myocardial injury, infarction and mortality in patients undergoing elective PCI: a pooled analysis of patientlevel data. Eur Heart J, 42(4):323–334. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa885
Song YF, Wang BC, Zhu XL, et al., 2021. Human umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs exosome attenuate myocardial injury by inhibiting ferroptosis in acute myocardial infarction mice. Cell Biol Toxicol, 37:51–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-020-09530-8
Stamenkovic A, O’Hara KA, Nelson DC, et al., 2021. Oxidized phosphatidylcholines trigger ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 320(3):H1170–H1184. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00237.2020
Stenseth K, Thyberg J, 1989. Monensin and chloroquine inhibit transfer to lysosomes of endocytosed macromolecules in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Eur J Cell Biol, 49(2):326–333.
Sugezawa K, Morimoto M, Yamamoto M, et al., 2022. GPX4 regulates tumor cell proliferation via suppressing ferroptosis and exhibits prognostic significance in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res, 42(12):5719–5729. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.16079
Sui MX, Xu D, Zhao WY, et al., 2021. CIRBP promotes ferroptosis by interacting with ELAVL1 and activating ferritinophagy during renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J Cell Mol Med, 25(13):6203–6216. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16567
Sun YM, Bao QC, Xuan BQ, et al., 2018. Human cytomegalovirus protein pUL38 prevents premature cell death by binding to ubiquitin-specific protease 24 and regulating iron metabolism. J Virol, 92(13):e00191–18. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00191-18
Tadokoro T, Ikeda M, Ide T, et al., 2020. Mitochondria-dependent ferroptosis plays a pivotal role in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. JCI Insight, 5(9):e132747. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.132747
Taher AT, Porter JB, Kattamis A, et al., 2016. Efficacy and safety of iron-chelation therapy with deferoxamine, deferiprone, and deferasirox for the treatment of iron-loaded patients with nontransfusion-dependent thalassemia syndromes. Drug Des Devel Ther, 10:4073–4078. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S117080
Tang DL, Chen X, Kang R, et al., 2021. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res, 31(2):107–125. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1
Tang LJ, Luo XJ, Tu H, et al., 2021a. Ferroptosis occurs in phase of reperfusion but not ischemia in rat heart following ischemia or ischemia/reperfusion. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 394(2):401–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01932-z
Tang LJ, Zhou YJ, Xiong XM, et al., 2021b. Ubiquitin-specific protease 7 promotes ferroptosis via activation of the p53/TfR1 pathway in the rat hearts after ischemia/reperfusion. Free Radic Biol Med, 162:339–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.10.307
Tang MZ, Chen Z, Wu D, et al., 2018. Ferritinophagy/ferroptosis: iron-related newcomers in human diseases. J Cell Physiol, 233(12):9179–9190. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26954
Tang MZ, Huang Z, Luo XL, et al., 2019. Ferritinophagy activation and sideroflexin1-dependent mitochondria iron overload is involved in apelin-13-induced cardiomyocytes hypertrophy. Free Radic Biol Med, 134:445–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.01.052
Tang SC, Gao F, Chen HM, et al., 2020. The role of iron, its metabolism and ferroptosis in traumatic brain injury. Front Cell Neurosci, 14:590789. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.590789
Tsubouchi K, Araya J, Yoshida M, et al., 2019. Involvement of GPx4-regulated lipid peroxidation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis pathogenesis. J Immunol, 203(8):2076–2087. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1801232
Tu C, Ortega-Cava CF, Winograd P, et al., 2010. Endosomalsorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) pathway-dependent endosomal traffic regulates the localization of active src at focal adhesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107(37):16107–16112. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1009471107
van Bergen JMG, Li X, Hua J, et al., 2016. Colocalization of cerebral iron with amyloid beta in mild cognitive impairment. Sci Rep, 6:35514. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35514
von Haehling S, Jankowska EA, van Veldhuisen DJ, et al., 2015. Iron deficiency and cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol, 12(11):659–669. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2015.109
Wang H, Jiang XJ, 2023. cGASing mitochondria to fend off ferroptosis. Cell Res, 33(4):263–264. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-023-00791-6
Wang K, Chen XZ, Wang YH, et al., 2022. Emerging roles of ferroptosis in cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Discov, 8:394. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-022-01183-2
Wang SY, Wang L, Qin X, et al., 2020. ALDH2 contributes to melatonin-induced protection against APP/PS1 mutation-prompted cardiac anomalies through cGAS-STING-TBK1-mediated regulation of mitophagy. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 5:119. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-0171-5
Wang YQ, Zhao YJ, Ye T, et al., 2021. Ferroptosis signaling and regulators in atherosclerosis. Front Cell Dev Biol, 9:809457. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.809457
Wang Z, Li YN, Ye YZ, et al., 2023. NLRP3 inflammasome deficiency attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Brain Res Bull, 193:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.11.016
Wu WW, Sato K, Koike A, et al., 2010. HERC2 is an E3 ligase that targets BRCA1 for degradation. Cancer Res, 70(15):6384–6392. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1304
Xiao LL, Ma XZ, Ye LQ, et al., 2022. IL-9/STAT3/fatty acid oxidation-mediated lipid peroxidation contributes to Tc9 cell longevity and enhanced antitumor activity. J Clin Invest, 132(7):e153247. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI153247
Xie YC, Hou T, Liu JY, et al., 2023. Autophagy-dependent ferroptosis as a potential treatment for glioblastoma. Front Oncol, 13:1091118. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1091118
Xiong HM, 2013. ZnO nanoparticles applied to bioimaging and drug delivery. Adv Mater, 25(37):5329–5335. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201301732
Xiong QH, Li X, Li WJ, et al., 2021. WDR45 mutation impairs the autophagic degradation of transferrin receptor and promotes ferroptosis. Front Mol Biosci, 8:645831. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.645831
Xiong W, Wang L, Yu FL, 2014. Regulation of cellular iron metabolism and its implications in lung cancer progression. Med Oncol, 31(7):28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0028-2
Xiu ZR, Zhu YL, Han JC, et al., 2022. Caryophyllene oxide induces ferritinophagy by regulating the NCOA4/FTH1/LC3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Pharmacol, 13:930958. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.930958
Yan HF, Zou T, Tuo QZ, et al., 2021. Ferroptosis: mechanisms and links with diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 6:49. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00428-9
Yang ND, Tan SH, Ng S, et al., 2014. Artesunate induces cell death in human cancer cells via enhancing lysosomal function and lysosomal degradation of ferritin. J Biol Chem, 289(48):33425–33441. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.564567
Yang SH, Wang XX, Contino G, et al., 2011. Pancreatic cancers require autophagy for tumor growth. Genes Dev, 25(7):717–729. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.2016111
Yang SS, Lian GJ, 2020. ROS and diseases: role in metabolism and energy supply. Mol Cell Biochem, 467(1–2):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03667-9
Yang XJ, Zhong XM, Tanyi JL, et al., 2013. mir-30d Regulates multiple genes in the autophagy pathway and impairs autophagy process in human cancer cells. Biochem Biophy Res Commun, 431(3):617–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.083
Yang XZ, Li XX, Zhang YJ, et al., 2016. Rab1 in cell signaling, cancer and other diseases. Oncogene, 35(44):5699–5704. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.81
Yang YY, Zhang K, Huang SF, et al., 2022. Apelin-13/APJ induces cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by activating the Pannexin-1/P2X7 axis and FAM134B-dependent reticulophagy. J Cell Phys, 237(4):2230–2248. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30685
Yi JM, Zhu JJ, Wu J, et al., 2020. Oncogenic activation of PI3K-AKT-mToR signaling suppresses ferroptosis via SREBP-mediated lipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 117(49):31189–31197. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2017152117
Yoo SE, Chen LJ, Na R, et al., 2012. Gpx4 ablation in adult mice results in a lethal phenotype accompanied by neuronal loss in brain. Free Radic Biol Med, 52(9):1820–1827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.02.043
Yu XX, Ruan Y, Shen T, et al., 2020. Dexrazoxane protects cardiomyocyte from doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by modulating miR-17-5p. BioMed Res Int, 2020:5107193. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5107193
Yu Y, Yan Y, Niu FL, et al., 2021. Ferroptosis: a cell death connecting oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Discov, 7:193. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00579-w
Zalpoor H, Akbari A, Jazi NN, et al., 2022. Possible role of autophagy induced by COVID-19 in cancer progression, chemo-resistance, and tumor recurrence. Infect Agents Cancer, 17:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13027-022-00450-2
Zhang H, Ma GS, Yao YY, et al., 2012. Olmesartan attenuates the impairment of endothelial cells induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein through downregulating expression of LOX-1. Int J Mol Sci, 13(2):1512–1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13021512
Zhang HY, Wang Z, Liu ZX, et al., 2021. Protective effects of dexazoxane on rat ferroptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy through regulating HMGB1. Front Cardiovasc Med, 8:685434. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.685434
Zhang J, Wang XY, Guan BY, et al., 2023. Qing-Xin-Jie-Yu Granule inhibits ferroptosis and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the GPX4/xCT signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol, 301:115852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2022.115852
Zhang PY, Park HJ, Zhang J, et al., 2020. Translation of the intrinsically disordered protein α-synuclein is inhibited by a small molecule targeting its structured mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 117(3):1457–1467. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1905057117
Zhao WK, Zhou Y, Xu TT, et al., 2021. Ferroptosis: opportunities and challenges in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021:9929687. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9929687
Zheng JS, Sato M, Mishima E, et al., 2021. Sorafenib fails to trigger ferroptosis across a wide range of cancer cell lines. Cell Death Dis, 12(7):698. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03998-w
Zhuo XZ, Wu Y, Ni YJ, et al., 2013. Isoproterenol instigates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and heart failure via AMPK inactivation-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. Apoptosis, 18(7):800–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0843-5
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82204389 and 82000454), the Medical Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province (No. SBGJ202103079), and the Henan Medical Science and Technology Joint Building Program (Nos. LHGJ20230283, LHGJ20190236, LHGJ20190227, LHGJ20190092, LHGJ20200310, and LHGJ20200284), China. We thank the Home for Researchers (https://www.home-for-researchers.com) for their language modification service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yi LUAN contributed to the conception of the study. Yi LUAN and Yang YANG contributed significantly to data analysis and manuscript preparation. Yang YANG, Kaidi REN, Bo QIN, and Hengdao LIU wrote the manuscript. Kaidi REN, Bo QIN, Hengdao LIU, Yi LUAN, and Yang YANG provided ideas and financial support for the review. Ying LUAN, Hui LIU, Han XING, and Jinyan PEI helped perform the analysis with constructive discussion and provided substantive guidance on the paper’s ideas and the entire writing process. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Yi LUAN, Yang YANG, Ying LUAN, Hui LIU, Han XING, Jinyan PEI, Hengdao LIU, Bo QIN, and Kaidi REN declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This review does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, Y., Yang, Y., Luan, Y. et al. Targeting ferroptosis and ferritinophagy: new targets for cardiovascular diseases. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 25, 1–22 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300097
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300097