干旱气象 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 519-526.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-04-0519
我国干旱半干旱区近60 a气象干旱气候特征分析
- 1.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,中国气象局干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730020
2.兰州资源环境职业技术大学,甘肃 兰州 730021
3.兰州区域气候中心,甘肃 兰州 730020
-
收稿日期:2023-11-23修回日期:2024-06-17出版日期:2024-08-31发布日期:2024-09-13 -
通讯作者:朱飙(1972—),男,正高级工程师,主要从事气候变化研究。E-mail:zhubiaolz@sohu.com 。 -
作者简介:李春华(1973—),女,副教授,主要从事气象教学与研究。E-mail:Lch1908@lzre.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42230611);中国气象局兰州干旱研究所干旱气象科学研究基金项目(IAM202208)
Analysis of climatic characteristics of meteorological drought in arid and semi-arid regions of China in recent 60 years
LI Chunhua1,2( ), ZHU Biao3(
), ZHU Biao3( ), YANG Jinhu1, HUANG Pengcheng3
), YANG Jinhu1, HUANG Pengcheng3
- 1. Institute of Arid Meteorology,China Meteorological Administration,Key Laboratory of Arid Climate Change and Reducing Disaster of Gansu Province,Key Laboratory of Arid Climate Change and Disaster Reduction of CMA,Lanzhou 730020,China
2. Lanzhou Resources & Environment Voc-Tech University, Lanzhou 730021, China
3. Lanzhou Regional Climate Center, Lanzhou 730020, China
-
Received:2023-11-23Revised:2024-06-17Online:2024-08-31Published:2024-09-13
摘要:
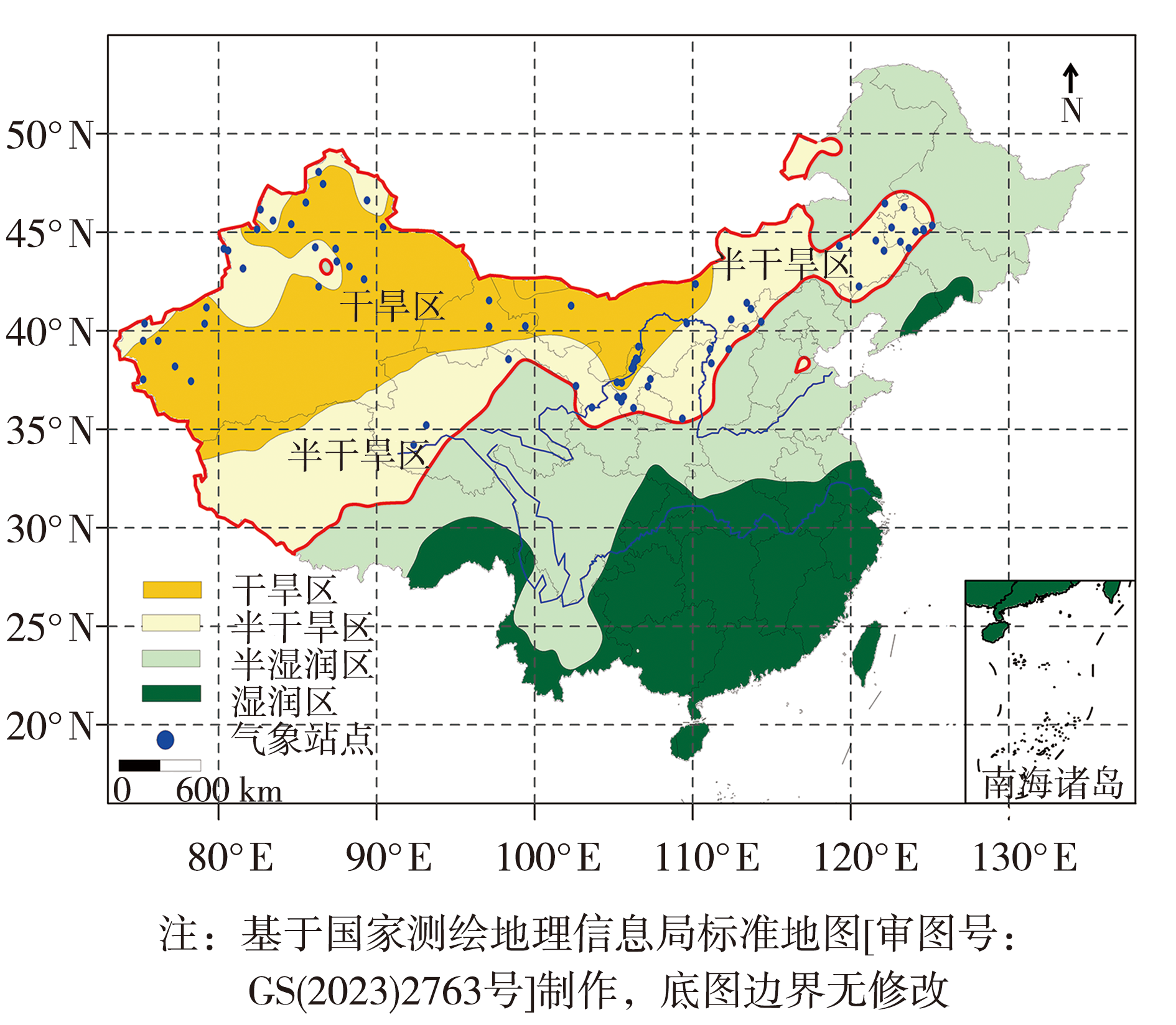
为研究我国干旱半干旱区连续无雨日气候特征的变化趋势,利用该区域74个气象站1961—2022年逐日降水观测资料,对研究区连续无雨日变化特征及其在1961—1990年和1991—2020年前后两个时段的差异等进行分析,重点关注16 d及以上连续无雨日,并将16~25 d、26~40 d、41~60 d、60 d以上连续无雨日分别定义为轻旱、中旱、重旱和特旱。结果表明:我国干旱半干旱气候区16 d及以上连续无雨日的发生次数和日数存在明显差异,尤其是重旱、特旱对应的连续无雨日发生次数和日数,干旱区分别是半干旱区的2.0倍与6.0倍左右;1991—2020年与1961—1990年相比,研究区西部不同等级气象干旱发生次数明显减少,而中东部有所增加;研究区西部不同等级干旱发生日数同样减少明显,中部轻旱和中旱发生日数减少,而重旱和特旱发生日数有所增加;研究时段内,该区域绝大部分气象站点不同等级干旱发生次数和日数均未发生突变。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李春华, 朱飙, 杨金虎, 黄鹏程. 我国干旱半干旱区近60 a气象干旱气候特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 519-526.
LI Chunhua, ZHU Biao, YANG Jinhu, HUANG Pengcheng. Analysis of climatic characteristics of meteorological drought in arid and semi-arid regions of China in recent 60 years[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 519-526.
使用本文
| 气候区 | 时段 | 连续无雨日 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1~5 d | 6~10 d | 11~15 d | 16~25 d (轻旱) | 26~40 d (中旱) | 41~60 d (重旱) | 60 d以上 (特旱) | ||
| 干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 13.1 | 5.7 | 2.9 | 2.7 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 1991—2020年 | 14.1 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| 半干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 28.2 | 8.3 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| 1991—2020年 | 27.7 | 8.6 | 3.5 | 2.6 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
表1 The average frequency of consecutive dry days with different grades in arid and semi-arid areas of China during 1961-1990 and 1991-2020 单位:次
Tab.1
| 气候区 | 时段 | 连续无雨日 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1~5 d | 6~10 d | 11~15 d | 16~25 d (轻旱) | 26~40 d (中旱) | 41~60 d (重旱) | 60 d以上 (特旱) | ||
| 干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 13.1 | 5.7 | 2.9 | 2.7 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 1991—2020年 | 14.1 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| 半干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 28.2 | 8.3 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| 1991—2020年 | 27.7 | 8.6 | 3.5 | 2.6 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| 气候区 | 时段 | 连续无雨日 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1~5 d | 6~10 d | 11~15 d | 16~25 d (轻旱) | 26~40 d (中旱) | 41~60 d (重旱) | 60 d以上 (特旱) | ||
| 干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 34.3 | 43.6 | 36.7 | 52.2 | 48.6 | 38.7 | 77.1 |
| 1991—2020年 | 36.2 | 46.3 | 37.9 | 53.5 | 43.1 | 39.8 | 77.2 | |
| 半干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 69.3 | 62.8 | 43.7 | 48.2 | 34.2 | 21.3 | 13.2 |
| 1991—2020年 | 68.4 | 65.6 | 43.9 | 49.6 | 32.0 | 19.6 | 14.7 | |
表2 The cumulative days of consecutive dry days with different grades in arid and semi-arid areas of China during 1961-1990 and 1991-2020 单位:d
Tab.2
| 气候区 | 时段 | 连续无雨日 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1~5 d | 6~10 d | 11~15 d | 16~25 d (轻旱) | 26~40 d (中旱) | 41~60 d (重旱) | 60 d以上 (特旱) | ||
| 干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 34.3 | 43.6 | 36.7 | 52.2 | 48.6 | 38.7 | 77.1 |
| 1991—2020年 | 36.2 | 46.3 | 37.9 | 53.5 | 43.1 | 39.8 | 77.2 | |
| 半干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 69.3 | 62.8 | 43.7 | 48.2 | 34.2 | 21.3 | 13.2 |
| 1991—2020年 | 68.4 | 65.6 | 43.9 | 49.6 | 32.0 | 19.6 | 14.7 | |
| 气候区 | 时段 | 连续无雨日 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1~5 d | 6~10 d | 11~15 d | 16~25 d (轻旱) | 26~40 d (中旱) | 41~60 d (重旱) | 60 d以上 (特旱) | ||
| 干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 2.6 | 7.7 | 12.8 | 19.6 | 31.7 | 48.8 | 94.1 |
| 1991—2020年 | 2.6 | 7.7 | 12.7 | 19.6 | 31.9 | 48.9 | 101.6 | |
| 半干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 2.5 | 7.6 | 12.7 | 19.6 | 31.5 | 48.5 | 90.8 |
| 1991—2020年 | 2.5 | 7.6 | 12.7 | 19.5 | 31.7 | 47.9 | 92.7 | |
表3 The average duration of consecutive dry days with different grades in arid and semi-arid regions of China during 1961-1990 and 1991-2020 单位:d
Tab.3
| 气候区 | 时段 | 连续无雨日 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1~5 d | 6~10 d | 11~15 d | 16~25 d (轻旱) | 26~40 d (中旱) | 41~60 d (重旱) | 60 d以上 (特旱) | ||
| 干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 2.6 | 7.7 | 12.8 | 19.6 | 31.7 | 48.8 | 94.1 |
| 1991—2020年 | 2.6 | 7.7 | 12.7 | 19.6 | 31.9 | 48.9 | 101.6 | |
| 半干旱区 | 1961—1990年 | 2.5 | 7.6 | 12.7 | 19.6 | 31.5 | 48.5 | 90.8 |
| 1991—2020年 | 2.5 | 7.6 | 12.7 | 19.5 | 31.7 | 47.9 | 92.7 | |

图2 1961—2020年我国干旱区(左)半干旱区(右)不同等级干旱发生次数年际变化
Fig.2 The inter-annual variation of frequency of drought with different grades in arid (the left) and semi-arid (the right) climate regions of China during 1961-2020

图3 1961—2020年我国干旱区(左)、半干旱区(右)不同等级干旱发生日数年际变化
Fig.3 The inter-annual variation of occurrence days of drought with different grades in arid (the left) and semi-arid (the right) region of China during 1961-2020
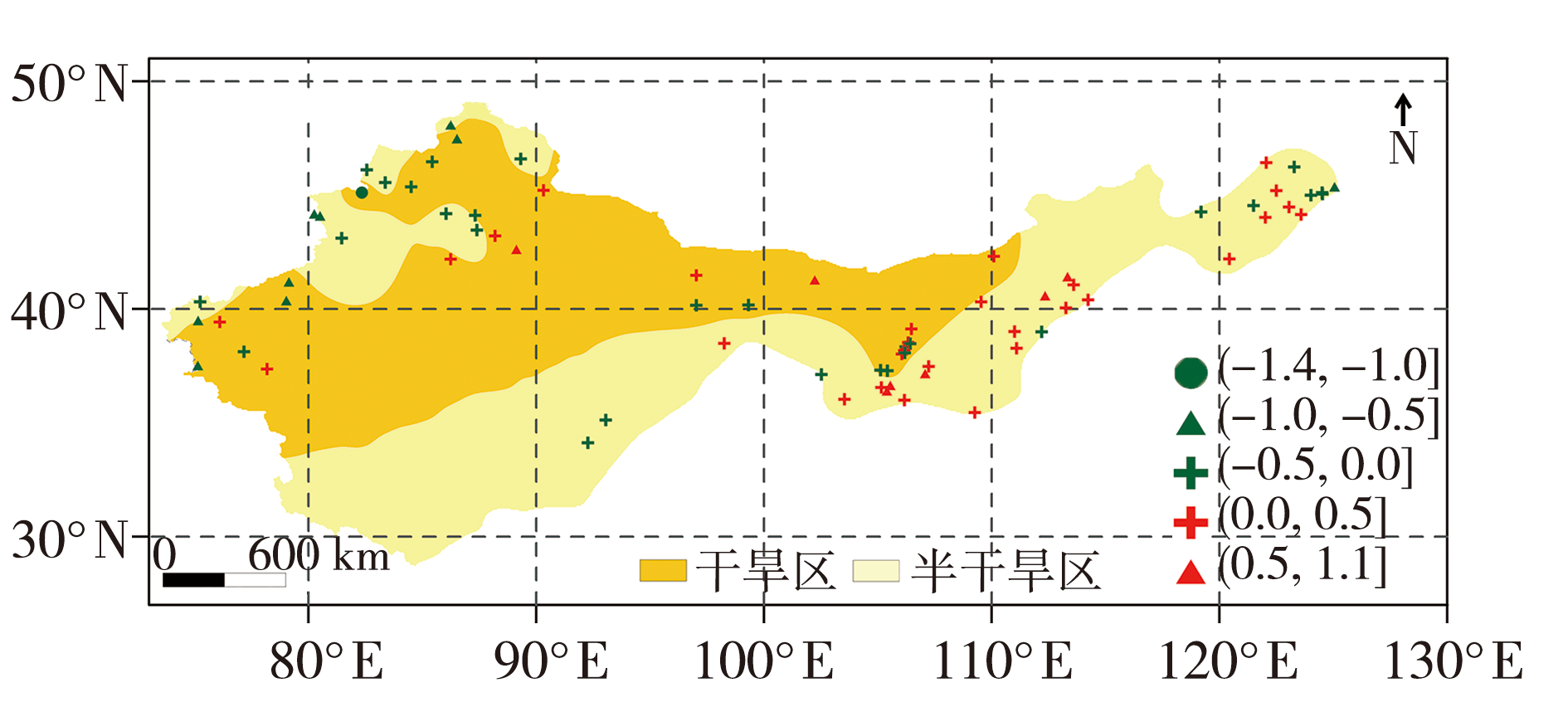
图4 1991—2020年与1961—1990年我国干旱半干旱区干旱发生总次数差值的空间分布(单位:次)
Fig.4 The spatial distribution of the difference between the total number of droughts in arid and semi-arid regions of China from 1991 to 2020 and from 1961 to 1990 (Unit: times)

图5 1991—2020年与1961—1990年我国干旱半干旱气候区轻旱(a)、中旱(b)、重旱(c)、特旱(d)发生日数差值的空间分布(单位:d)
Fig.5 The spatial distribution of the difference of the occurrence days of partial drought (a), moderate drought (b), severe drought (c) and extreme drought (d) between 1991-2020 and 1961-1990 in the arid and semi-arid climate regions of China (Unit: d)
| 干旱等级 | 发生次数检验 | 发生日数检验 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | |
| 轻旱 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 中旱 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| 重旱 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 特旱 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
表4 1961—1990年和1991—2020年我国干旱半干旱区不同等级干旱发生次数、日数平均值差异的显著性检验
Tab.4 The significance test of difference of mean frequency and occurrence days of different grades drought between 1961-1990 and 1991-2020 in arid and semi-arid regions of China
| 干旱等级 | 发生次数检验 | 发生日数检验 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | |
| 轻旱 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 中旱 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| 重旱 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 特旱 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 |

图6 1961—1990年与1991—2020年我国干旱半干旱气候区降水(a)和潜在蒸散(b)平均值差异的显著性检验
Fig.6 The significance test of difference of mean precipitation (a) and potential evapotranspiration (b) between 1961-1990 and 1991-2020 in arid and semi-arid climate regions of China
| [1] | 柏庆顺, 颜鹏程, 蔡迪花, 等, 2019. 近56 a中国西北地区不同强度干旱的年代际变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(5): 722-728. |
| [2] | 丁一汇, 王绍武, 郑景云, 等, 2013. 中国气候[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 402-405. |
| [3] | 段亚雯, 2015. 中国区域连续无降水日数的变化及其与季节性干旱的联系[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. |
| [4] | 符淙斌, 安芷生, 2002. 我国北方干旱化研究: 面向国家需求的全球变化科学问题[J]. 地学前缘, 9(2): 271-275. |
| [5] | 符淙斌, 马柱国, 2023. 全球干旱/半干旱区年代尺度干湿变化研究的进展及思考[J]. 大气科学学报, 46(4): 481-490. |
| [6] | 顾颖, 刘静楠, 林锦, 2010. 近60年来我国干旱灾害情势和特点分析[J]. 水利水电技术, 41(1): 71-74. |
| [7] | 郝立生, 何丽烨, 马宁, 等, 2023. 厄尔尼诺事件年际变化与我国华北夏季干旱的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 41(6): 829-840. |
| [8] | 黄嘉佑, 2004. 气象统计分析与预报方法[M]. 3版. 北京: 气象出版社: 19-20. |
| [9] | 黄晚华, 隋月, 杨晓光, 等, 2014. 基于连续无有效降水日数指标的中国南方作物干旱时空特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 30(4): 125-135. |
| [10] |
黄小燕, 王小平, 王劲松, 等, 2014. 中国大陆1960-2012年持续干旱日数的时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 32(3): 326-333.
DOI |
| [11] | 李茂松, 李森, 李育慧, 2003. 中国近50年旱灾灾情分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 24(1): 7-10. |
| [12] | 李宗梅, 张增祥, 赵晓丽, 等, 2017. 全国干湿分布区动态变化研究[J]. 地球与环境, 45(4): 420-433. |
| [13] | 刘莉红, 翟盘茂, 郑祖光, 2008. 中国北方夏半年最长连续无降水日数的变化特征[J]. 气象学报, 66(3): 474-477. |
| [14] |
刘炜, 赵艳丽, 高晶, 等, 2024. 2022年7月内蒙古干旱半干旱区涝—旱转折事件的成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(1): 11-18.
DOI |
| [15] | 吕星玥, 荣艳淑, 石丹丹, 2019. 长江中下游地区2010/2011年秋冬春连旱成因再分析[J]. 干旱气象, 37(2): 198-208. |
| [16] |
马鹏里, 杨金虎, 卢国阳, 等. 2020. 西北地区东部气候的转折性变化[J]. 高原气象, 39(4): 840-850.
DOI |
| [17] | 马柱国, 符淙斌, 2005. 中国干旱和半干旱带的10年际演变特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(3): 519-525. |
| [18] | 马柱国, 符淙斌, 2006. 1951—2004年中国北方干旱化的基本事实[J]. 科学通报, 51(20): 2429-2439. |
| [19] | 施雅风, 沈永平, 胡汝骥, 2002. 西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的信号、影响和前景初步探讨[J]. 冰川冻土, 24(3): 219-226. |
| [20] | 施雅风, 沈永平, 李栋梁, 等, 2003. 中国西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的特征和趋势探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 23(2): 152-164. |
| [21] |
王胜, 张强, 张良, 等, 2024. 旱区陆面非降水性水分研究进展和展望[J]. 干旱气象, 42(1): 1-10.
DOI |
| [22] | 王莺, 王劲松, 姚玉璧, 等, 2014. 中国华南地区持续干期日数时空变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(1): 86-94. |
| [23] | 王芝兰, 周甘霖, 张宇, 等, 2019. 美国干旱监测预测业务发展及其科学挑战[J]. 干旱气象, 37(2): 183-197. |
| [24] | 谢祥永, 2014. 中国北方干旱化的时空变化特征[C]// 中国气象学会. 第31届中国气象学会年会S5干旱灾害风险评估与防控. |
| [25] | 苑全治, 吴绍洪, 戴尔阜, 等, 2017. 1961—2015年中国气候干湿状况的时空分异[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 47(11): 1 339-1 348. |
| [26] | 张存杰, 廖要明, 段居琦, 等, 2016. 我国干湿气候区划研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 12(4): 261-267. |
| [27] | 张强, 杨金虎, 王朋岭, 等, 2023. 西北地区气候暖湿化的研究进展与展望[J]. 科学通报, 58(68): 1 814-1 828. |
| [28] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 500-521. |
| [29] |
张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2015. 中国西北地区干旱气象灾害监测预警与减灾技术研究进展及其展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 30(2): 196-213.
DOI |
| [30] | 张强, 朱飙, 杨金虎, 等, 2021. 西北地区气候湿化趋势的新特征[J]. 科学通报, 56(66): 3 757-3 771. |
| [31] | 中华人民共和国水利部, 2016. 区域旱情等级: GB/T 32135—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [32] | 朱飙, 张强, 李春华, 等, 2023. 我国干旱半干旱区气候变化特征及其对干湿波动的影响[J]. 大气科学学报, 46(1): 42-54. |
| [33] | ALLEN R G, PEREIRA L S, RAES D, et al, 1998. Crop evapotranspiration-Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56[M]. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. |
| [34] | ALLEN R G, PRUITT W O, WRIGHT J L, et al, 2006. A recommendation on standardized surface resistance for hourly calculation of reference ET0 by the FAO56 Penman-Monteith method[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 81(1/2): 1-22. |
| [35] | DUAN Y W, MA Z G, YANG Q, 2017. Characteristics of consecutive dry days variations in China[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 130(1): 701-709. |
| [36] | GONG D Y, WANG J A, HAN H, 2005. Trends of summer dry spells in China during the late twentieth century[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 88(3): 203-214. |
| [37] | HEIM R R, 2002. A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the United States[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 83(8): 1 149-1 165. |
| [38] | HULME M, MARSH R, JONES P D, 1992. Global changes in a humidity index between 1931-60 and 1961-90[J]. Climate Research, 2: 1-22. |
| [39] | LEI Y H, DUAN A M, 2011. Prolonged dry episodes and drought over China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 31(12): 1 831-1 840. |
| [40] |
SHI J, CUI L L, WEN K M, et al, 2018. Trends in the consecutive days of temperature and precipitation extremes in China during 1961-2015[J]. Environmental Research, 161: 381-391.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | YANG J, GONG D Y, WANG W S, et al, 2012. Extreme drought event of 2009/2010 over southwestern China[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 115(3): 173-184. |
| [42] | ZENG Z X, SUN J Q, 2021. Characteristics of spring consecutive dry days with different durations across China based on the objective zoning approach[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 22(7), 1 035-1 041. |
| [43] | ZHANG Q, YANG J H, DUAN X Y, et al, 2022. The eastward expansion of the climate humidification trend in northwest China and the synergistic influences on the circulation mechanism[J]. Climate Dynamics, 59: 2 481-2 497. |
| [1] | 苏宏梅, 张 楠, 冉新民, 康 超.
干旱半干旱区中小流域洪水机器学习预警模型及其应用
[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 683-693. |
| [2] | 武强, 毕淼, 何佳洋, 韩旭, 李艳丽, 阳园燕. 1991—2020年重庆水稻生育期连阴雨气候特征及成因[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 629-636. |
| [3] | 王胜, 张强, 张良, 王兴, 杜昊霖, 曾剑, 问晓梅. 旱区陆面非降水性水分研究进展和展望[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 1-10. |
| [4] | 刘炜, 赵艳丽, 高晶, 李林惠, 王慧敏. 2022年7月内蒙古干旱半干旱区涝—旱转折事件的成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 11-18. |
| [5] | 罗晓玲, 杨梅, 赵慧华, 李岩瑛, 蒋菊芳, 伏芬琪. 厄尔尼诺事件对甘肃武威温度降水以及气象干旱影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 849-859. |
| [6] | 马思源, 金燕, 张思, 王楚钦, 马志敏. 厄尔尼诺/南方涛动事件对云南秋季气象干旱的不同影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 860-872. |
| [7] | 王昀, 王丽娟, 陆晓娟, 张金玉, 王芝兰, 沙莎, 胡蝶, 杨扬, 颜鹏程, 李忆平. 2023年上半年我国干旱的特征及其成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 884-896. |
| [8] | 赵惠珍, 何涛, 郭瑞霞, 王成福, 张艳荣, 李琪. 基于SPEI的甘南高原气象干旱变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 688-696. |
| [9] | 张金丹, 刘明春, 李兴宇, 丁文魁, 杨华, 蒋菊芳. 石羊河流域干湿气候变化特征及对NDVI的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 697-704. |
| [10] | 王莹, 张舒, 徐永清, 阙粼婧, 李新华, 黄英伟, 陈雪, 王蕾. 近50 a黑龙江省5—9月气象干旱及大气环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 540-549. |
| [11] | 姜舒婕, 程莹, 方楠, 周毓荃, 单中华, 张磊. 基于干旱和水位特征构建水库人工增雨需求指数[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 341-349. |
| [12] | 薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 1-13. |
| [13] | 李芳红, 张晓煜, 冯蕊, 陈仁伟, 张亚红, 卫建国. 宁夏贺兰山东麓葡萄园小气候特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 284-295. |
| [14] | 刘新伟,王澄海,郭润霞,杨晓军,狄潇泓. 1981—2018年甘肃省极端暴雨天气过程的气候与环流特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 750-758. |
| [15] | 潘卫华, 余永江, 罗艳艳, 张琳琳, 杨志勇. 基于地基GPS大气可降水量的福建水汽资源时空分布特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(4): 577-584. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 654
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 216
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||