Abstract
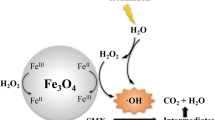
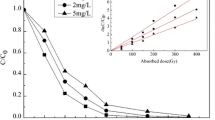
The presence of sulfonamide antibiotics in aquatic environments has received increasing attention in recent years. Sulfadiazine (SD), a widely used heterocyclic sulfonamide pharmaceutical, has entered into the receiving water body. In this paper, gamma rays are used to irradiate samples of sulfadiazine antibiotics-containing wastewater. The results demonstrate that SD can be effectively degraded by irradiation, but the mineralization degree of SD (in terms of TOC) is not as efficient as the SD degradation. The addition of Fe2+ can significantly enhance the SD degradation and mineralization through the generation of hydroxyl radical by catalytic decomposition of H2O2 from water radiolysis. Ion chromatography analysis indicates that sulfate ions (SO4 2−) and formate (HCOO−) are the main intermediate products. Gamma irradiation is a promising technology for removing low-concentration antibiotics from water and wastewater.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.L. Boreen, X.A. Arnold, K. McNeill, Photochemical fate of sulfa drugs in the aquatic environment: sulfa drugs containing five-membered heterocyclic groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 3933–3940 (2004). doi:10.1021/es0353053
C.G. Daughton, T.A. Ternes, Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: agents of subtle change? Environ. Health Perspect. 107, 907–938 (1999). doi:10.2307/3434573
P. Drzewicz, M. Trojanowicz, R. Zona et al., Decomposition of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by ozonation, ionizing radiation as well as ozonation combined with ionizing radiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 69, 281–287 (2004). doi:10.1016/S0969-806X(03)00471-7
M.J. García-Galán, S.G. Blanco, R.L. Roldán et al., Ecotoxicity evaluation and removal of sulfonamides and their acetylated metabolites during conventional wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 437, 403–412 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.08.038
N. Getoff, S. Solar, Radiation induced decomposition of chlorinated phenols in water. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 31, 121–130 (1988)
N. Getoff, Comparison of radiation and photoinduced degradation of pollutants in water: synergistic effect of O2, O3 and TiO2: a short review. Res. Chem. Intermed. 27, 343–358 (2001). doi:10.1163/156856701104202228
Z.B. Guo, F. Zhou, Y.F. Zhao et al., Gamma irradiation-induced sulfadiazine degradation and its removal mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 191, 256–262 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.03.012
S.J. He, J.L. Wang, L.F. Ye et al., Removal of diclofenac from surface water by electron beam irradiation combined with a biological aerated filter. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 105, 104–108 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2014.05.019
V. Homem, L. Santos, Degradation and removal methods of antibiotics from aqueous matrices—a review. J. Environ. Manag. 92, 2304–2347 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.05.023
J. Hu, J.L. Wang, R. Cheng, Degradation of chlorophenols in aqueous solution by γ-radiation and ozone oxidation. Sci. China B Chem. 49, 186–192 (2006). doi:10.1007/s11426-006-0186-y
J. Hu, J.L. Wang, Degradation of chlorophenols in aqueous solution by gamma radiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 76, 1489–1492 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2007.02.058
J.M. Joseph, B.S. Choi, P. Yakabuskie et al., A combined experimental and model analysis on the effect of pH and O2 (aq) on γ-radiolytically produced H2 and H2O2. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 77, 1009–1020 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2008.06.001
Y.K. Liu, J. Hu, J.L. Wang, Fe2+ enhancing sulfamethazine degradation in aqueous solution by gamma irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 96, 81–87 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2013.08.018
Y.K. Liu, J.L. Wang, Degradation of sulfamethazine by gamma irradiation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 250, 99–105 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.01.050
Y.K. Liu, J. Hu, J.L. Wang, Radiation-induced removal of sulphadiazine antibiotics from wastewater. Environ. Technol. 35, 2028–2034 (2014). doi:10.1080/09593330.2014.889761
Y.X. Peng, S.J. He, J.L. Wang et al., Comparison of different chlorophenols degradation in aqueous solutions by gamma irradiation under reducing conditions. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 81, 1629–1633 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2012.04.011
M. Trojanowicz, P. Drzewicz, P. Panta et al., Radiolytic degradation and toxicity changes in γ-irradiated solutions of 2,4,-dichlorophenol. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 65, 357–366 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0969-806X(02)00336-5
J.L. Wang, L.J. Xu, Advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: formation of hydroxyl radical and application. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 251–325 (2012). doi:10.1080/10643389.2010.507698
J.L. Wang, J.Z. Wang, Application of radiation technology to sewage sludge processing: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 143, 2–7 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.027
J. Xue, J.L. Wang, Radiolysis of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in aqueous solution by gamma radiation. J. Environ. Sci. 20, 1153–1157 (2008). doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62203-2
S.Q. Yu, J. Hu, J.L. Wang, Gamma radiation-induced degradation of p-nitrophenol (PNP) in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 177, 1061–1067 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.028
R. Zona, S. Schmid, S. Solar, Detoxification of aqueous chlorophenol solutions by ionizing radiation. Water Res. 33, 1314–1319 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00319-4
H.P. Liu, X.D. Hu, X.H. Zhang et al., Study on γ-radiolytical degradation of oxytetracycline in aqueous solution and its degradation pathway. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 1, 010301 (2015). doi:10.11889/j.1000-3456.2015.rrj.33.010301. (in Chinese)
W.B. Jia, Y.Q. He, Y.S. Ling et al., Study on the degradation of cyclohexanebutyric acid in aqueous solution by γ-ray irradiation. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 5, 050301 (2014). doi:10.11889/j.1000-3456.2014.rrj.32.050301. (in Chinese)
W.B. Jia, Y.H. Wei, J.G. Liu et al., Studying the treatment effect of γ-rays combined with H2O2 on landfill leachate. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 1, 010402 (2013). (in Chinese)
L.N. Li, Y.X. Liu, H.Y. Bao, Elimination of dichloroacetic acid in deaerated aqueous solutions by 60Co- rays irradiation. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 31, 010305(5) (2013). (in Chinese)
Z. Huang, Y.X. Liu, H.Y. Bao, 60Co-ray irradiation degradation of dilute aqueous solution of imidacloprid. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 31, 050301(8) (2013). (in Chinese)
H.Y. Gao, Y.X. Liu, H.Y. Bao, The investigation of acephate degradation in oxygen saturated aqueous solution by 60Co γ-irradiation. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 30(2), 76–80 (2012). (in Chinese)
L. Chi, Y.M. Ha, F. Wang et al., Effects of γ-irradiation on degradation of Ochratoxin A in aqueous solution. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 29(1), 61–64 (2011). (in Chinese)
M. Zheng, G. Xu, L. Zhao et al., Comparison of EB-radiolysis and UV/H2O2-degradation of CBZ in pure water and solutions. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 26, 020302 (2015). doi:10.13538/j.1001-8042/nst.26.20302
Y. Zhou, C.Q. Cao, M. Wang, Bromate formation in bromide-containing waters irradiated by gamma rays. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 25, 010301 (2014)
L.F. Ye, S.J. He, C.P. Yang et al., Comparison of pilot scale electron beam and bench scale gamma irradiations of cyanide aqueous in solution. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 24, S010202 (2013)
L. Wang, M.H. Wu, G. Xu et al., Radiolytic degradation and mechanism study of electron beam-irradiated solutions of 4-tert-octylphenol. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 23, 295–304 (2012)
N. Liu, G. Xu, J. Ma et al., E-beam radiolysis of aqueous dimethyl phthalate solution. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 22, 35–38 (2011)
L. Wojnárovits, E. Takács, Rate coefficients of hydroxyl radical reactions with pesticide molecules and related compounds: a review. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 96, 120–134 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2013.09.003
S. Colak, M. Korkmaz, Investigation of radiosterilization and dosimetric features of sulfacetamide sodium. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 36, 791–798 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2004.08.036
S. Colak, M. Korkmaz, Kinetics of the radicals induced in gamma irradiated sulfafurazole: an EPR study. Z. Naturforsch. A J. Phys. Sci. 59, 481–487 (2004)
H.Y. Kim, O.M. Lee, T.H. Kim et al., Enhanced biodegradability of pharmaceuticals and personal care products by ionizing radiation. Water Environ. Res. 87, 321–325 (2015). doi:10.2175/106143014X14062131178033
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51338005).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Z., Wang, JL. Removal of sulfonamide antibiotics from wastewater by gamma irradiation in presence of iron ions. NUCL SCI TECH 27, 104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-016-0109-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-016-0109-3