Abstract
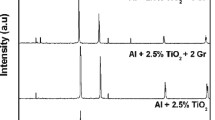
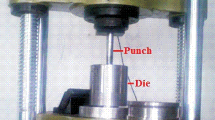
The cold upsetting studies were carried out for the aluminium metal matrix hybrid composites in the present study. Aluminium metal matrix hybrid composites were synthesised through powder metallurgy route from ball-milled powders to yield the following compositions: Al + 2.5 wt% TiO2 + 2 wt% Gr, Al + 2.5 wt% TiO2 + 4 wt% Gr, Al + 5.0 wt% TiO2 + 2 wt% Gr and Al + 5.0 wt% TiO2 + 4 wt% Gr. The compaction process was carried out using suitable punch and die in 40 kN hydraulic press, and sintering was done in an electric muffle furnace at the temperature of 590 °C for 3 h. The sintered preforms were subjected to incremental compressive loading of 10 kN until the cracks were found at the free surface. The true axial stress, true hoop stress, true hydrostatic stress and true effective stress were calculated for all the preforms, and all these stresses are correlated with the true axial strain. The stress ratio parameters (σ z/σ eff, σ θ/σ eff, σ z/σ m and σ θ/σ m) of the all preforms were correlated with true axial strain. The maximum true axial stress, true hoop stress, true effective stress and hydrostatic static stress are obtained for the composite containing 5 wt% of TiO2 and 4 wt% of graphite and the minimum ones are obtained for composite containing 2.5 wt% of TiO2 and 2 wt% of graphite.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan TX, Zhang D, Yang G, Toshiya Shibayanagi, Massaki Naka. Fabrication of in situ Al2O3/Al composite via remelting. J Mater Process Technol. 2003;142(2):556.
Ahamed Hafeez, Senthilkumar V. Consolidation behavior of mechanically alloyed aluminum based nanocomposites reinforced with nanoscale Y2O3/Al2O3 particles. Mater Charact. 2011;62(12):1235.
Mohammad Amin Baghchesara, Hossein Abdizadeh. Microstructural and mechanical properties of nanometric magnesium oxide particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites produced by powder metallurgy method. J Mech Sci Technol. 2012;26(2):367.
Ravindran P, Manisekar K, Narayanasamy P, Selvakumar N, Narayanasamy R. Application of factorial techniques to study the wear of Al hybrid composites with graphite addition. Mater Des. 2012;39:42.
Mao CH, Sun XD, Liang QS, Yang J, Du J. Interfacial reaction process of the hot-pressed WC/2024Al composite. Rare Met. 2013;32(4):397.
Sivasankaran S, Sivaprasad K, Narayanasamy R, Vijay Kumar Iyer. Synthesis, structure and sinterability of 6061 AA100−x −x wt% TiO2 composites prepared by high-energy ball milling. J Alloys Compd. 2010;491(1–2):712.
Akhlaghi F, Pelaseyyed SA. Characterization of aluminum/graphite particulate composites synthesized using a novel method termed “in situ powder metallurgy”. Mater Sci Eng A. 2004;385(1–2):258.
Mahdavi S, Akhlaghi F. Effect of the graphite content on the tribological behavior of Al/Gr and Al/30SiC/Gr composites processed by in situ powder metallurgy (IPM) method. Tribol Lett. 2011;44(1):1.
Manchang Gui, Suk Bong Kang. Aluminum hybrid composite coatings containing SiC and graphite particles by plasma spraying. Mater Lett. 2001;51(5):396.
Wu XF, Zhang GG, Wu FF. Microstructure and dry sliding wear behavior of cast Al–Mg2Si in situ metal matrix composite modified by Nd. Rare Met. 2013;32(3):284.
Altunpak Yahya, Ay Mustafa, Aslan Serdar. Drilling of a hybrid Al/SiC/Gr metal matrix composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2011;60(5–8):513.
Ted-Guo ML, Tsao CYA. Tribological behavior of self-lubricating aluminium/SiC/graphite hybrid composites synthesized by the semi-solid powder-densification method. Compos Sci Technol. 2000;60(1):65.
Narayanasamy R, Ramesh T, Pandey KS, Pandey SK. Effect of particle size on new constitutive relationship of aluminium–iron powder metallurgy composite during cold upsetting. Mater Des. 2008;29(5):1011.
Narayanasamy R, Ramesh T, Pandey KS. Some aspects on cold forging of aluminium–alumina powder metallurgy composite under triaxial stress state condition. Mater Des. 2008;29(6):1212.
Sivasankaran S, Narayanasamy R, Ramesh T, Prabhakar M. Analysis of workability behavior of Al–SiC P/M composites using backpropagation neural network model and statistical technique. Comput Mater Sci. 2009;47(1):46.
Randall German M. Metal Powder Industries Federation. II ed. Princeton: Powder Metallurgy Science; 1984. 174.
Ramesh T, Prabhakar M, Narayanasamy R. Workability studies on Al–5 % SiC powder metallurgycomposite during cold upsetting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2009;44(3–4):389.
Acknowledgments
The authours would like to thank Chendhuran College of Engineering and Technology for permitting to carry out the experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravichandran, M., Naveen Sait, A. & Anandakrishnan, V. Al–TiO2–Gr powder metallurgy hybrid composites with cold upset forging. Rare Met. 33, 686–696 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0239-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0239-x