Abstract
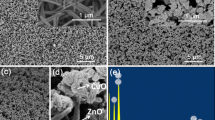
We fabricate a flexible hybrid nanogenerator (HNG), based on multilayered nanocomposite materials, which integrates a piezoelectric nanogenerator (PENG) and a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) into a single structure with only two electrodes. The HNG enables enhancement of the electrical output of the nanogenerators. An open-circuit voltage of 280 V and a short-circuit current of 25 μA are achieved by a HNG of 2.5 cm × 2.5 cm in size, superior to the performance of previously reported HNGs. In addition, the energy-conversion process of the HNG relies on the working mechanism of both the PENG and TENG. The polarization direction and doping content of BTO are the two major factors that affect the electrical output. Biomechanical energy harvesting from walking motion or the bending of an arm is also demonstrated.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Z. L.; Song, J. H. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246.
Fan, F. R.; Tian, Z. Q.; Wang, Z. L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334.
Qi, Y.; McAlpine, M. C. Nanotechnology-enabled flexible and biocompatible energy harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1275–1285.
Lee, K. Y.; Gupta, M. K.; Kim, S.-W. Transparent flexible stretchable piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators for powering portable electronics. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 139–160.
Zhang, X. S.; Han, M. D.; Meng, B.; Zhang, H. X. High performance triboelectric nanogenerators based on large-scale mass-fabrication technologies. Nano Energy 2015, 11, 304–322.
Meng, B.; Tang, W.; Too, Z. H.; Zhang, X. S.; Han, M. D.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. X. A transparent single-friction-surface triboelectric generator and self-powered touch sensor. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3235–3240.
Wang, Z. L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L. Progress in triboelectric nanogenerators as a new energy technology and selfpowered sensors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2250–2282.
Seung, W.; Gupta, M. K.; Lee, K. Y.; Shin, K. S.; Lee, J. H.; Kim, T. Y.; Kim, S.; Lin, J.; Kim, J. H.; Kim, S.-W. Nanopatterned textile-based wearable triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3501–3509.
Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T. J.; Jing, Q. S.; Wang, Z. L. Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3426.
Shin, S.-H.; Kwon, Y. H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Jung, J.-Y.; Lee, M. H.; Nah, J. Triboelectric charging sequence induced by surface functionalization as a method to fabricate high performance triboelectric generators. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4621–4627.
Zi, Y. L.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. H.; Chen, J.; Fan, X.; Yang, P.-K.; Yi, F.; Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric–pyroelectric–piezoelectric hybrid cell for high-efficiency energy-harvesting and self-powered sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2340–2347.
Jung, W.-S.; Kang, M.-G.; Moon, H. G.; Baek, S.-H.; Yoon, S.-J.; Wang, Z. L.; Kim, S.-W.; Kang, C.-Y. High output piezo/triboelectric hybrid generator. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9309.
Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Zi, Y. L.; Zhou, P. F.; Lin, J.; Guo, H. Y.; Xu, Y. L.; Wang, Z. L. All-plastic-materials based self-charging power system composed of triboelectric nanogenerators and supercapacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1070–1076.
Wang, S. H.; Wang, Z. L.; Yang, Y. A one-structure-based hybridized nanogenerator for scavenging mechanical and thermal energies by triboelectric–piezoelectric–pyroelectric effects. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2881–2887.
Shi, B. J.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, W.; Yan, L.; Wang, X. X.; Liu, H.; Yao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. L. A packaged self-powered system with universal connectors based on hybridized nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 846–852.
Kimura, Y.; Mizusawa, N.; Ishii, A.; Yamanari, T.; Ono, T. Changes of low-frequency vibrational modes induced by universal 15N- and 13C-isotope labeling in S2/S1 FTIR difference spectrum of oxygen-evolving complex. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 13170–13177.
Garczarek, F.; Gerwert, K. Functional waters in intraprotein proton transfer monitored by FTIR difference spectroscopy. Nature 2006, 439, 109–112.
Zeng, Z. H.; Jin, H.; Chen, M. J.; Li, W. W.; Zhou, L. C.; Zhang, Z. Lightweight and anisotropic porous MWCNT/ WPU composites for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 303–310.
Shin, M. K.; Oh, J.; Lima, M.; Kozlov, M. E.; Kim, S. J.; Baughman, R. H. Elastomeric conductive composites based on carbon nanotube forests. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2663–2667.
Liu, C.-X.; Choi, J.-W. Patterning conductive PDMS nanocomposite in an elastomer using microcontact printing. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 085019.
Amjadi, M.; Pichitpajongkit, A.; Lee, S.; Ryu, S.; Park, I. Highly stretchable and sensitive strain sensor based on silver nanowire-elastomer nanocomposite. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5154–5163.
Imai, A.; Nagarajan, V.; Takahashi, R.; Lippmaa, M.; Matsumoto, Y. Self-template growth of ferroelectric Bi4Ti3O12 nanoplates via flux-mediated epitaxy with VOx. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 5233–5237.
Gu, H. S.; Hu, Z. L.; Hu, Y. M.; Yuan, Y.; You, J.; Zou, W. D. The structure and photoluminescence of Bi4Ti3O12 nanoplates synthesized by hydrothermal method. Colloid. Surf. A 2008, 315, 294–298.
Chen, X. H.; Hu, J. Q.; Chen, Z. W.; Feng, X. M.; Li, A. Q. Nanoplated bismuth titanate sub-microspheres for protein immobilization and their corresponding direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3448–3454.
Wang, F.; Wang, J. B.; Zhong, X. L.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Wu, D.; Mo, D.; Guo, D. Y.; Yuan, S. G.; Zhang, K. D. et al. Shape-controlled hydrothermal synthesis of ferroelectric Bi4Ti3O12 nanostructures. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 1397–1403.
Chen, Z. W.; He, X. H. Low-temperature preparation of nanoplated bismuth titanate microspheres by a sol–gelhydrothermal method. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 497, 312–315.
Han, M. D.; Chen, X. X.; Yu, B. C.; Zhang, H. X. Coupling of piezoelectric and triboelectric effects: From theoretical analysis to experimental verification. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500187.
Park, K.-I.; Lee, M.; Liu, Y.; Moon, S.; Hwang, G.-T.; Zhu, G.; Kim, J. E.; Kim, S. O.; Kim, D. K.; Wang, Z. L. et al. Flexible nanocomposite generator made of BaTiO3 nanoparticles and graphitic carbons. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2999–3004.
Park, K.-I.; Jeong, C. K.; Ryu, J.; Hwang, G.-T.; Lee, K. J. Flexible and large-area nanocomposite generators based on lead zirconate titanate particles and carbon nanotubes. Adv. Energy. Mater. 2013, 3, 1539–1544.
Meng, X. S.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z. L. Robust thin-film generator based on segmented contact electrification for harvesting wind energy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 8011–8016.
Chandrashekar, B. N.; Deng, B.; Smitha, A. S.; Chen, Y. B.; Tan, C. W.; Zhang, H. X.; Peng, H. L.; Liu, Z. F. Rollto- roll green transfer of CVD graphene onto plastic for a transparent and flexible triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5210–5216.
Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Jun, K.-W.; Kim, J.-H.; Seung, W.-C.; Kwon, O. H.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Oh, I.-K. Silk nanofiber-networked bio-triboelectric generator: Silk bio-TEG. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1502329.
Wang, Y.-L.; Wang, X.-Y.; Chu, L.-Z.; Deng, Z.-C.; Liang, W.-H.; Liu, B.-T.; Fu, G.-S.; Wongdamnern, N.; Sareein, T.; Yimnirun, R. Simulation of hysteresis loops for polycrystalline ferroelectrics by an extensive Landau-type model. Phys. Lett. A 2009, 373, 4282–4286.
Chen, B.; Zuo, Z. H.; Liu, Y. W.; Zhan, Q.-F.; Xie, Y. L.; Yang, H. L.; Dai, G. H.; Li, Z. X.; Xu, G. J.; Li, R.-W. Tunable photovoltaic effects in transparent Pb(Zr0.53, Ti0.47)O3 capacitors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 173903.
Niu, S. M.; Wang, X. F.; Yi, F.; Zhou, Y. S.; Wang, Z. L. A universal self-charging system driven by random biomechanical energy for sustainable operation of mobile electronics. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8975.
Yang, P.-K.; Lin, L.; Yi, F.; Li, X. H.; Pradel, K. C.; Zi, Y. L.; Wu, C.-I.; He, J.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. L. A flexible, stretchable and shape-adaptive approach for versatile energy conversion and self-powered biomedical monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3817–3824.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Chinese “thousands talents” program for pioneer researcher and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51572030), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 2162047), and Chongqing Natural Science and Foundation (No. cstc2016jcyjA0621).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2016_1331_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Multilayered flexible nanocomposite for hybrid nanogenerator enabled by conjunction of piezoelectricity and triboelectricity
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Su, L., Kuang, S. et al. Multilayered flexible nanocomposite for hybrid nanogenerator enabled by conjunction of piezoelectricity and triboelectricity. Nano Res. 10, 785–793 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1331-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1331-3